Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Imazono, Takashi; Yanagihara, Mihiro*
Photon Factory News, 22(3), p.18 - 22, 2004/11
Using soft-X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy with photon incidence at a critical angle of total reflection, it was made clear that SiO existed within a depth of a few nanometers from the surface of Fe/Si multilayers. It was generated by oxidation of the interdiffused Fe
existed within a depth of a few nanometers from the surface of Fe/Si multilayers. It was generated by oxidation of the interdiffused Fe Si layer nearest to the topmost Fe layer. Consequently, the Fe
Si layer nearest to the topmost Fe layer. Consequently, the Fe Si layer was found to decrease in thickness. This result suggests that the total-reflection soft-X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy is fairly useful to analyze the chemical state of elements to a depth of a few nanometers from the surface.
Si layer was found to decrease in thickness. This result suggests that the total-reflection soft-X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy is fairly useful to analyze the chemical state of elements to a depth of a few nanometers from the surface.
 in granite matrix
in granite matrixYamaguchi, Tetsuji; Nakayama, Shinichi; Kawada, Chiharu*
Genshiryoku Bakkuendo Kenkyu, 9(1), p.61 - 66, 2002/09
The effective diffusivity (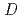
 ) and distribution ratio (
) and distribution ratio (
 ) of
) of  Ba
Ba in Inada granite have been determined by the through-diffusion method. Experiments were performed in triplicate for 10
in Inada granite have been determined by the through-diffusion method. Experiments were performed in triplicate for 10 , 1 and 10 mol m
, 1 and 10 mol m BaCl
BaCl solutions at 25
solutions at 25 C. The
C. The 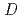
 value obtained at a BaCl
value obtained at a BaCl concentration of 10 mol m
concentration of 10 mol m , agreed to the estimated value based on the pore diffusion model. The lower BaCl
, agreed to the estimated value based on the pore diffusion model. The lower BaCl concentrations yielded higher
concentrations yielded higher 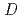
 values and higher
values and higher 
 values. The variation in
values. The variation in 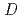
 was neither due to the speciation of barium in the solutions nor due to variation in physical properties of the pore structure in the rock. Contribution of diffusion in sorbed state should be responsible for the variation in
was neither due to the speciation of barium in the solutions nor due to variation in physical properties of the pore structure in the rock. Contribution of diffusion in sorbed state should be responsible for the variation in 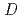
 .
.
Yamaguchi, Tetsuji; Nakayama, Shinichi
JAERI-Conf 2002-004, p.325 - 332, 2002/03
When long-lived radionuclides are transported by groundwater through fractures in the rock mass surrounding a radioactive waste repository, their diffusion into pores in the rock matrix and ensuing sorption onto mineral surfaces are expected to retard their transport along the pathways. We have characterized the pore structure of the Japanese Inada biotite granite and confirmed that Fick's diffusion law can be applied to the transport of aqueous species in granite. Effective diffusivity was determined by the through-diffusion method for cationic, anionic and actinide complex species to explore the mechanism of diffusion of the aqueous species. The results of this study enable us to provide a scientifically sound basis for radionuclide diffusion in granite for performance assessment of geological disposal. Future studies should emphasize understanding the diffusion mechanisms in low-permeability engineered barrier materials, data acquisition on long-term degradation of the materials and quantifying uncertainties associated with long-term mass transport analysis.
Nakamura, Hirofumi; Hayashi, Takumi; Kakuta, Toshiya*; Suzuki, Takumi; Nishi, Masataka
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 297(3), p.285 - 291, 2001/09
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:74.75(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The isotope effect on the implantation-driven permeation of pure tritium (T) and deuterium (D) through nickel was investigated, respectively. The rate-determining processes of backward flow at the upstream surface and permeation at the down-stream surface were found to be as follows: recombination on up-stream surface and diffusion at down-stream side in a lower temperature region, whereas recombination on both surfaces in a higher temperature region for T and D, respectively. The diffusion coefficients of T and D derived by analyzing the obtained transient data of permeation in the lower temperature region were in good agreement with literature data of deuterium. The obtained activation energy of diffusion for T and D suggested the tendency of mass dependence. The surface recombination coefficients for both isotopes were also derived and showed in good agreement with literature data. As a result, the experimental results indicated the surface recombination could be attributed to the isotope effect of the permeation between T and D rather than the diffusion.
Sato, Tadashi
Radiochimica Acta, 46, p.101 - 108, 1989/00
no abstracts in English
JAERI-M 83-052, 66 Pages, 1983/03
no abstracts in English
; ; *
Trans.Faraday Soc., 57, P. 2018, 1961/00
no abstracts in English